The Fascinating History of the Human-Dog Relationship: From Wolves to Companion Animals
The history of dog domestication dates back thousands of years. While it is difficult to determine exact dates, it is estimated that the domestication of dogs took place between 20,000 and 40,000 years ago.
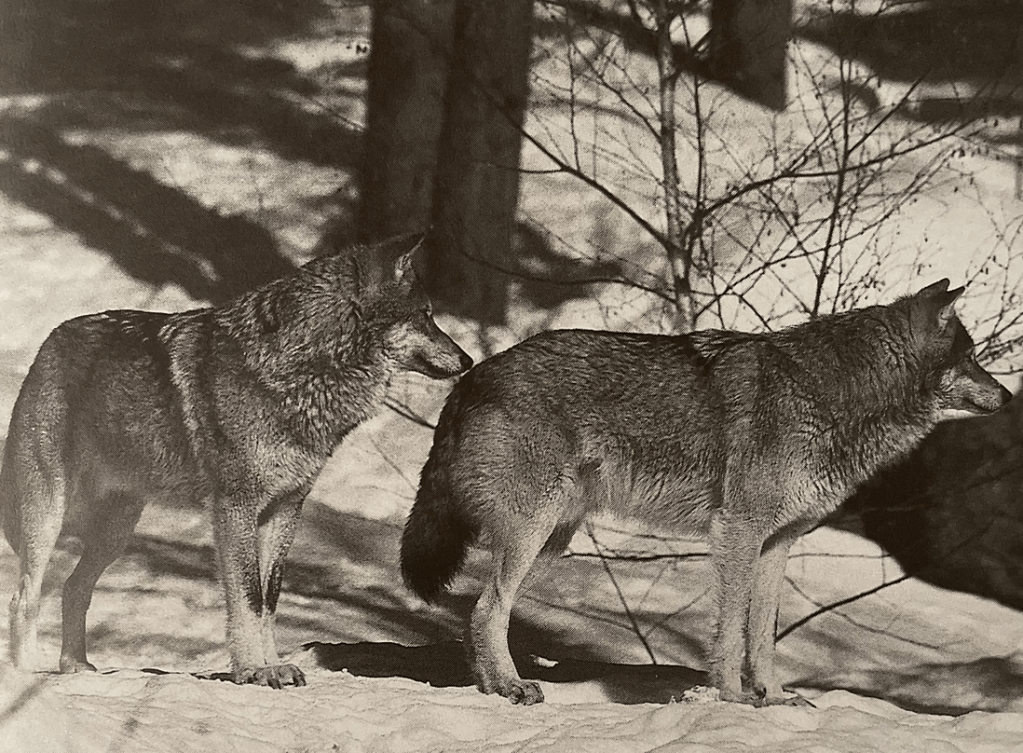
The ancestors of dogs were likely wolves that lived in close proximity to human settlements. People may have started tolerating and feeding wolves due to their hunting skills, which led to a symbiotic relationship.
Over time, people began selectively breeding certain wolves based on favorable traits such as obedience, vigilance, or specific abilities. This process of selective breeding resulted in the formation of different dog breeds with unique characteristics.
Dogs quickly became more than just working animals. They became companions, hunting and herding partners, and eventually, beloved pets. Dogs played significant roles in various cultures and were valued for their loyalty, intelligence, and versatility.
The relationship between humans and dogs has evolved and strengthened throughout the centuries. Dogs are now kept as pets and service animals worldwide, playing important roles in aspects of human life such as therapy, search and rescue operations, security, and pure enjoyment.
The history of dog domestication is a fascinating story of collaboration and mutual benefit between humans and animals, resulting in the diversity of dog breeds we know today.
Domestic dogs descend from gray wolves through selective breeding and prolonged interaction.

The domestic dog descends from the gray wolf (Canis lupus). Scientific research has shown that the gray wolf is the closest relative to our domesticated dogs. While the exact timing and location of domestication are still subjects of investigation, it is widely believed that the gray wolf is the ancestor of the modern dog.
Origin of Dogs: A Blend of Wild Wolf Species
The ancestors of modern dogs are believed to have descended from various wolf species, including the gray wolf (Canis lupus), the dingo (Canis lupus dingo), the coyote (Canis latrans), and possibly the Eurasian wolf (Canis lupus lupus). These wolf species played a role in the emergence of early dog breeds.

(C)2023, SC Luna Nera